自移式液压支架外文文献翻译、中英文翻译
翻译部分英文原文(见参考文献[19].P157)SELF-ADVANCINGHYDRAULICPOWEREDSUPPORTSModernlongwallminingemployshydraulicpoweredsupportsatthefacearea.Thesupportnotonlyholdsuptheroof,pushesthefacechainconveyor,andadvancesitself,butalsoprovidesasafeenvironmentforallassociatedminingactivities.Thereforeitssuccessfulselectiona...
相关推荐
-
碧桂园滨江府模板专项施工方案

 2022-11-24 183
2022-11-24 183 -
大型综合体地下室混凝土浇筑控制技术与重点--x

 2023-04-30 83
2023-04-30 83 -
JA建筑公司成本控制的问题与对策--x

 2023-04-30 118
2023-04-30 118 -
藏艺文博园规划设计中藏文化的保护传承--x

 2023-04-30 124
2023-04-30 124 -
不同类型加固工程与加固方案分析--x

 2023-04-30 130
2023-04-30 130 -
ZigBee技术下楼宇火灾自动报警平台的开发研究--x

 2023-04-30 122
2023-04-30 122 -
不同类型的房地产开发项目的类型与开发特点--x

 2023-04-30 364
2023-04-30 364 -
大连湾海底隧道工程的安全管理新思路和方法--x

 2023-04-30 246
2023-04-30 246 -
电梯等待时间最短的数学模型研究--x

 2023-04-30 207
2023-04-30 207 -
港珠澳大桥论文(参考研究范文6篇)--x

 2023-04-30 999+
2023-04-30 999+
相关内容
-
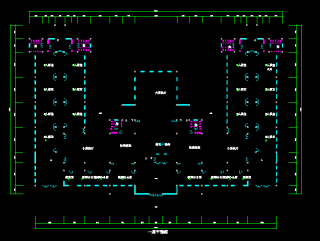
高层建筑电气设计
分类:土木建筑化工水利
时间:2023-09-20
标签:设计
格式:ZIP
价格:30 光币
-
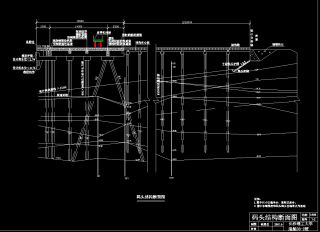
港件杂货港区总平面布置与码头结构设计
分类:土木建筑化工水利
时间:2023-10-07
标签:结构设计
格式:ZIP
价格:50 光币
-
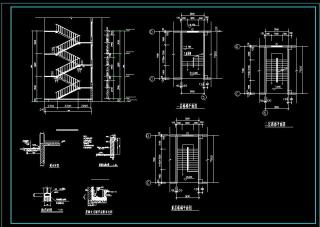
房屋建筑学-楼梯平面图-建筑大样图
分类:土木建筑化工水利
时间:2023-10-10
标签:无
格式:ZIP
价格:10 光币
-
基于6层建筑用电负荷等级(论文+DWG图纸+外文翻译+文献综述+开题报告)
分类:土木建筑化工水利
时间:2023-10-24
标签:开题报告
格式:ZIP
价格:30 光币
-
某厂房梯形钢屋架,采用1.5×6.0m预应力砼大型屋面板
分类:土木建筑化工水利
时间:2024-07-01
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:30 光币