注塑成型优化方法(有出处)--中英文翻译
Atechnicalnoteonthecharacterizationofelectroformednickelshellsfortheirapplicationtoinjectionmolds——UniversidaddeLasPalmasdeGranCanaria,DepartamentodeIngenieriaMecanica,SpainAbstractThetechniquesofrapidprototypingandrapidtoolinghavebeenwidelydevelopedduringthelastyears.Inthisarticle,electroformingasa...
相关推荐
-
论文提纲农业硕士论文写作中的常见问题及对策

 2023-07-07 37
2023-07-07 37 -
3854字论文写作指导商务英语论文大纲

 2023-07-07 45
2023-07-07 45 -
论文范文个人信用评价体系建设的现状及策略

 2023-07-07 33
2023-07-07 33 -
1141字论文写作指导毕业论文大纲

 2023-07-07 39
2023-07-07 39 -
3247字论文写作指导税务文书概要

 2023-07-07 20
2023-07-07 20 -
36142字硕士毕业论文杨希闵生活、朋友与文学作品研究

 2023-07-07 27
2023-07-07 27 -
34222字硕士毕业论文史传传统下的贾平凹小说研究——以强秦、鲁谷、戴登、老生为中心

 2023-07-07 36
2023-07-07 36 -
29542字硕士毕业论文韩少功的小说创作与湘西民间文学文化

 2023-07-10 41
2023-07-10 41 -
农业机械化概念界定与理论基础,农业机械狭义定义简介

 2023-07-19 31
2023-07-19 31 -
开题报告在线电磁钢轨探伤数据处理及信息管理方法研究

 2023-08-30 46
2023-08-30 46
相关内容
-

GB 3668.9-1983 组合机床通用部件 主轴部件尺寸
分类:课程设计课件资料
时间:2023-10-03
标签:无
格式:PDF
价格:5 光币
-

GB 3668.10-1983 组合机床通用部件 多轴箱主轴端部和可调接杆尺寸
分类:课程设计课件资料
时间:2023-10-03
标签:无
格式:PDF
价格:5 光币
-

W组合机床设计简明手册
分类:课程设计课件资料
时间:2023-10-03
标签:设计
格式:PDF
价格:5 光币
-

组合机床设计参考图册
分类:课程设计课件资料
时间:2023-10-03
标签:设计
格式:PDF
价格:5 光币
-
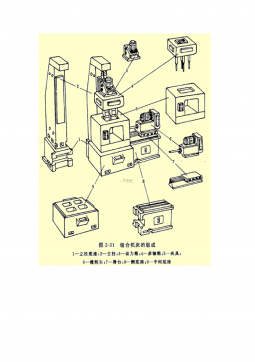
组合机床实例
分类:课程设计课件资料
时间:2023-10-03
标签:无
格式:DOC
价格:5 光币